Immigrant Share in Construction Sets New Record
Originally Published by: NAHB — November 20, 2024
SBCA appreciates your input; please email us if you have any comments or corrections to this article.
Reflecting the sharp increase in net immigration of recent years, the number of new immigrants joining the construction industry rose substantially in 2022. According to the latest American Community Survey (ACS), the industry managed to attract close to 130,000 new workers coming from outside the U.S. to help with persistent labor shortages. For comparison, this inflow surpasses the combined number of new immigrants who joined the industry in the two years prior to the pandemic. Only during the housing boom of 2005-2006, was the industry absorbing a similar number of new foreign-born workers.1
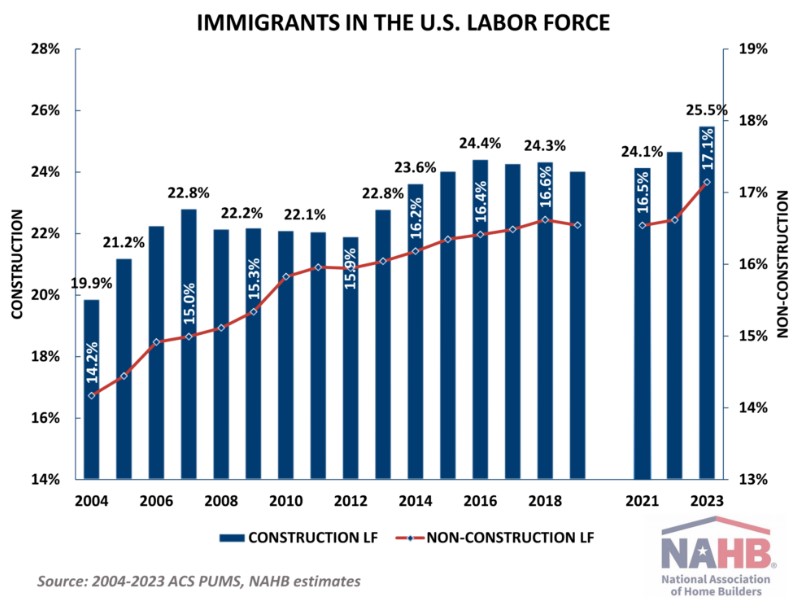
Native-born workers remain reluctant to join the industry, with their total count remaining below the record levels of the housing boom of the mid-2000s by over half a million. As a result, the share of immigrants in construction reached a new historic high of 25.5% in 2023. In construction trades, the share of immigrants remains even higher, with one in three craftsmen coming from outside the U.S. This is consistent with the earlier ACS data that regularly shows higher shares of immigrants in the construction trades.
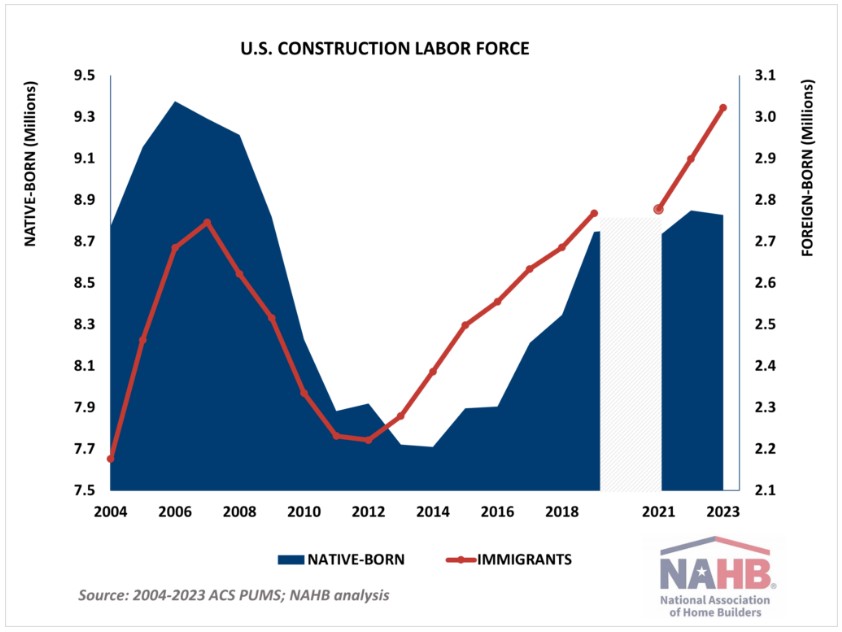
In 2023, 11.9 million workers, including both self-employed and temporarily unemployed, comprised the construction workforce. Out of these, 8.9 million were native-born, and 3 million were foreign-born, the highest number of immigrant workers in construction ever recorded by the ACS.
The construction labor force, including both native- and foreign-born workers, exceeds the pre-pandemic levels but remains smaller than during the housing boom of the mid-2000s. As the chart above illustrates, it is the native-born workers that remain missing. Compared to the peak employment levels of 2006, construction is short 550,000 native-born workers and new immigrants only partially close the gap. Due to the data collection issues during the early pandemic lockdown stages, we do not have reliable estimates for 2020 and omit these in the chart above.
Typically, the annual flow of new immigrant workers into construction is highly responsive to the changing labor demand. The number of newly arrived immigrants in construction rises rapidly when housing starts are rising and declines precipitously when the housing industry is contracting. The response of immigration is normally quite rapid, occurring in the same year as a change in construction activity. Statistically, the link is captured by high correlation between the annual flow of new immigrants into construction and measures of new home construction, especially new single-family starts.
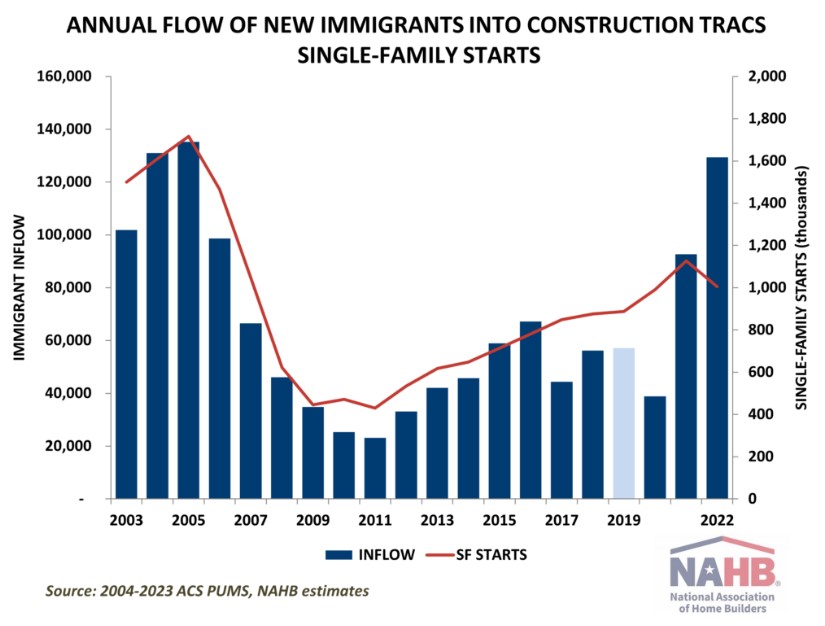
The latest data show that the substantial uptick in the number of new immigrants in 2022 does not reflect the changing volume of home building as new single-family starts declined during that time period.
Previously, the link between immigrant inflow and home building activity also disconnected in 2017 when NAHB’s estimates showed a surprising drop in the number of new immigrants in construction despite steady gains in housing starts. The connection was further severed by pandemic-triggered lockdowns and restrictions on travel and border crossings, drastically interrupting the flow of new immigrant workers. In 2021, however, the flow of immigrants into construction returned to typical levels driven by home building activity.
The overall rising trend and the noticeable uptick after the pandemic in the share of immigrants are consistent with but more pronounced in construction compared to broader U.S. economy. Excluding construction, where the reliance on foreign-born workers is greater, the share of immigrants in the U.S. labor force increased from just over 14% in 2004 to over 17% in 2023, the highest share recorded by the ACS.